Discover the top 10 agricultural technology trends reshaping farming, from AI and robotics to blockchain and climate resilience.

In today’s rapidly evolving agricultural landscape, technological advancements are reshaping traditional farming practices.
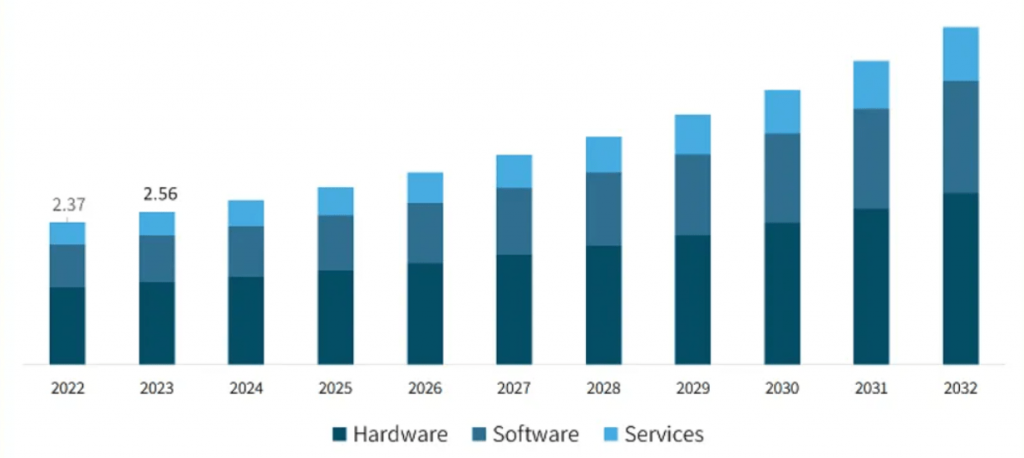
Digital Agriculture Market Share, By Component,2021-2032, (USD Billion)
From harnessing the power of AI to maximizing resource efficiency through smart farming techniques, here are the top ten trends driving innovation in agriculture:
Modern agriculture is embracing smart farming technologies like never before. Robots are transforming agriculture by performing critical tasks such as seeding, harvesting, packing, palletizing, and crop maintenance. They automate operations in large-scale farms, handling tasks like monitoring crop health, applying treatments, and managing livestock activities. This technology improves efficiency, addresses labor shortages, and ensures high-quality produce reaches the market, making it indispensable for modern agriculture’s success and sustainability.
The importance of Robotics has been recognized at national levels. On April 2024 The U.S. National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (USDA NIFA) decided to collaborate to pioneer foundational research in agricultural robotics.

Critical to modern farming operations, remote monitoring systems equipped with IoT sensors continuously track essential parameters such as soil moisture and temperature. This data-driven approach not only facilitates remote farm management but also enables automated control of irrigation systems. Farmers can ensure water is delivered precisely where and when it’s needed, maximizing crop productivity while conserving resources.
The global market for internet of things (IoT) in agriculture is poised for significant growth, surging from $27.1 billion in 2021 to a projected $84.5 billion by 2031. Asia’s rising population and food demands, along with government initiatives promoting smart farming technologies in the region made it the largest in the IoT market.
The Agricultural Sensor Market is expected to grow steadily, reaching an estimated USD 3.46 billion by 2029. This represents a significant increase from its USD 2.01 billion size in 2024, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5%. (Source: Mordor Intelligence)

Digital twins and generative AI are at the forefront of agricultural innovation, transforming how farmers plan and execute their operations. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical farming environments, allowing for detailed simulations and predictive analytics. Coupled with generative AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets, including historical weather patterns and soil conditions, farmers can make data-driven decisions to optimize planting schedules, crop management practices, and resource allocation.
GenAI technologies are easier to adopt because of applications like fieldWISE. Accessible through voice commands in the farmer’s native language, fieldWISE provides easy access to the latest agricultural developments and findings. Additionally, chatbots available on mobile phones with voice and text options further enhance information access, particularly for farmers in rural areas.



The push towards sustainability is driving the adoption of MRV systems in agriculture. These systems accurately measure, report, and verify greenhouse gas emissions reductions, supporting initiatives such as carbon credits and carbon neutrality pledges.
Carbon sequestration in agriculture refers to practices that capture and store carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and transfer it into agricultural land. There are two main ways this happens:
By demonstrating their environmental impact and adopting sustainable practices, farmers can access new revenue streams and contribute to global climate goals. Large food manufacturing and trading enterprises are increasingly including carbon monitoring in their sustainability goals and investing in technologies that can monitor the sequestration.
In conclusion, the integration of these cutting-edge technologies is transforming agriculture into a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient industry. Embracing these trends not only enhances farm productivity and profitability but also ensures food security and environmental stewardship for future generations.